Giao diện - Tkinter - Thread
Summary: in this tutorial, you’ll learn how to use multiple threads in Tkinter applications to make the applications more responsive.
When to use Thread in Tkinter applications
In a Tkinter application, the main loop should always start in the main thread. It’s responsible for handling events and updating the GUI.
If you have a background operation that takes time, you should execute it in a separate thread.
Otherwise, the application won’t be responsive. In the worst case, it will freeze while the operation is running.
To create and control multiple threads in Tkinter applications, you can use the Python threading module.
The threading module is included in Python’s standard library so you don’t need to install it.
For more information on how to use the threading module, you can follow the Python threading tutorial.
Tkinter thread example
We’ll build a simple program that downloads a webpage specified by an URL and displays its contents in a Text widget:
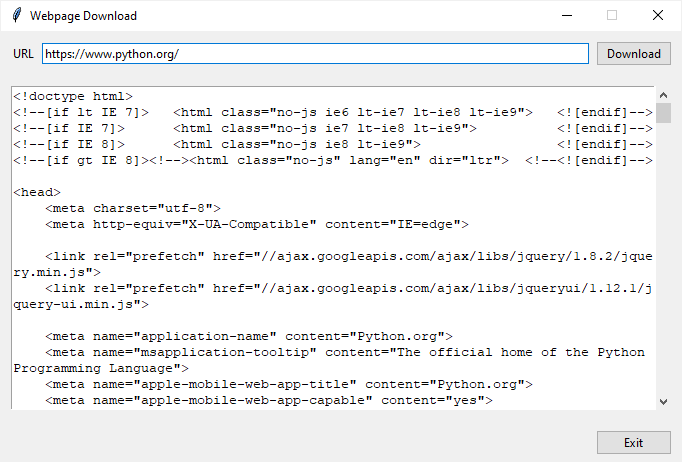
To download a webpage, we’ll use the requests module.
First, install the requests module by executing the following command:
pip install requests
Code language: Python (python)
Next, import tkinter, threading, and requests modules:
import tkinter as tk from tkinter import ttk from tkinter.messagebox import showerror from threading import Thread import requests
Code language: Python (python)
Then, define a new class called AsyncDownload that inherits from the Thread class:
class AsyncDownload(Thread): def __init__(self, url): super().__init__() self.html = None self.url = url def run(self): response = requests.get(self.url) self.html = response.text
Code language: Python (python)
How the AsyncDownload class works:
- In the
__init__()method of theAsyncDownloadclass, we initialize thehtmlandurlattributes. - In the
run()method, we call the get theget()function to download the webpage specified by the URL and assign the HTML source code to thehtmlattribute.
After that, create the App class inherits from the Tk class. The App class represents the root window.
The root window consists of three frames that hold all the widgets. We won’t focus on how to create widgets and place them on the window using the grid geometry manager.
When you click the download button, the program executes the handle_download() method of the App class.
In the handle_download() method, we check if the url is provided. If yes, we create a new instance of the AsyncDownload class and start the thread. Also, we disable the download button and clear the contents of the Text widget.
In addition, we call the monitor() method to monitor the status of the thread.
def handle_download(self): url = self.url_var.get() if url: self.download_button['state'] = tk.DISABLED self.html.delete(1.0, "end") download_thread = AsyncDownload(url) download_thread.start() self.monitor(download_thread) else: showerror(title='Error', message='Please enter the URL of the webpage.')
Code language: Python (python)
In the monitor() method, we schedule an action that will run the monitor() method after 100ms if the thread is still alive.
If the download completed, we update the contents for the Entry widget and re-enable the download button:
def monitor(self, thread): if thread.is_alive(): # check the thread every 100ms self.after(100, lambda: self.monitor(thread)) else: self.html.insert(1.0, thread.html) self.download_button['state'] = tk.NORMAL
Code language: Python (python)
Finally, run the application’s main loop:
if __name__ == "__main__": app = App() app.mainloop()
Code language: Python (python)
The following show the complete program:
import tkinter as tk from tkinter import ttk from tkinter.messagebox import showerror from threading import Thread import requests class AsyncDownload(Thread): def __init__(self, url): super().__init__() self.html = None self.url = url def run(self): response = requests.get(self.url) self.html = response.text class App(tk.Tk): def __init__(self): super().__init__() self.title('Webpage Download') self.geometry('680x430') self.resizable(0, 0) self.create_header_frame() self.create_body_frame() self.create_footer_frame() def create_header_frame(self): self.header = ttk.Frame(self) # configure the grid self.header.columnconfigure(0, weight=1) self.header.columnconfigure(1, weight=10) self.header.columnconfigure(2, weight=1) # label self.label = ttk.Label(self.header, text='URL') self.label.grid(column=0, row=0, sticky=tk.W) # entry self.url_var = tk.StringVar() self.url_entry = ttk.Entry(self.header, textvariable=self.url_var, width=80) self.url_entry.grid(column=1, row=0, sticky=tk.EW) # download button self.download_button = ttk.Button(self.header, text='Download') self.download_button['command'] = self.handle_download self.download_button.grid(column=2, row=0, sticky=tk.E) # attach the header frame self.header.grid(column=0, row=0, sticky=tk.NSEW, padx=10, pady=10) def handle_download(self): url = self.url_var.get() if url: self.download_button['state'] = tk.DISABLED self.html.delete(1.0, "end") download_thread = AsyncDownload(url) download_thread.start() self.monitor(download_thread) else: showerror(title='Error', message='Please enter the URL of the webpage.') def monitor(self, thread): if thread.is_alive(): # check the thread every 100ms self.after(100, lambda: self.monitor(thread)) else: self.html.insert(1.0, thread.html) self.download_button['state'] = tk.NORMAL def create_body_frame(self): self.body = ttk.Frame(self) # text and scrollbar self.html = tk.Text(self.body, height=20) self.html.grid(column=0, row=1) scrollbar = ttk.Scrollbar(self.body, orient='vertical', command=self.html.yview) scrollbar.grid(column=1, row=1, sticky=tk.NS) self.html['yscrollcommand'] = scrollbar.set # attach the body frame self.body.grid(column=0, row=1, sticky=tk.NSEW, padx=10, pady=10) def create_footer_frame(self): self.footer = ttk.Frame(self) # configure the grid self.footer.columnconfigure(0, weight=1) # exit button self.exit_button = ttk.Button(self.footer, text='Exit', command=self.destroy) self.exit_button.grid(column=0, row=0, sticky=tk.E) # attach the footer frame self.footer.grid(column=0, row=2, sticky=tk.NSEW, padx=10, pady=10) if __name__ == "__main__": app = App() app.mainloop()
Code language: Python (python)
Summary
- Do execute background tasks in separate threads to make the Tkinter application responsive.

